Discharges from the genitals in men are leaks from the urethra (urethra) and the secretion of preputial glands, which are located at the head of the penis, under the skin of the foreskin. The ejaculatory duct, prostate ducts, urethral and bulburetral glands open into the urethra.
In a healthy man, only urine and ejaculate flow through the urethra. This is physiological discharge from the penis and should not cause discomfort. Unfortunately, this is not always the case.
For various reasons, men's health is shaking and instead of normal secretions, abnormal leaks appear or urine and semen change.
Variants of physiological secretions
Criteria for normal discharge corresponding to the functions of the organs of the urogenital system:
- Urine - clear, from straw to yellow-gold color, practically odorless, containing no flakes or other inclusions;
- Prostate secretion has a viscous consistency and a white tinge, has a specific sperm odor;
- Ejaculation: semen from the ejaculatory duct mixes with secretions from the Littre (urethral), Cooper (bulbourethral) and prostatic glands, taking on a gray-white color and mucous consistency;
- Fresh smegma from the preputial glands is like a thick white fat; may turn yellow or green over time.
The preputial lubricant - smegma - is released continuously, accumulating under the inner layer of the foreskin and in the coronal groove of the penis. The lubricant consists of fatty and bacterial residues, distributes evenly and reduces friction between the foreskin and the gloss. Maximum activity of the preputial glands is natural in the period of puberty; with age, secretion decreases and stops completely from old age.
If you neglect the rules of personal hygiene, then smegma can accumulate under the folds of the foreskin. In this case, the fatty part of the lubricant is oxidized, and the protein part is decomposed (in fact, it is rotting), and the masses turn green, taking on an unpleasant odor. The same process occurs with phimosis, when, due to the melting of the foreskin, it is impossible to completely free the head of the penis from the folds of skin and remove the smegma. Accumulation and dissolution of the lubricant can lead to chronic balance and balanoposthitis (inflammation of the foreskin and glans penis), increasing the risk of developing tumors.
Urethral, mucous discharge, colorless from bulburetral and urethral glands. Discharge data appear in men with arousal-related arousal. The excretion of pure mucus aims to lubricate the urethra and improve sperm passage. The amount of secretion varies from minimal to abundant, these parameters are related to the individual characteristics of the organism and the frequency of sexual activity. After a prolonged abstinence, the volume of secretions increases.
Pollution is a spontaneous release of sperm, which is not associated with intercourse. It is usually seen in the morning when testosterone levels rise. It depends on the age and intensity of sexual activity: it appears in boys during puberty, in adult men - with irregular or infrequent intercourse.
Prostatorrhea, leakage from the urethra of a small amount of transparent mucus with white-gray inclusions. Occurs after abdominal muscle tension (for example, with constipation) or after urination. The secretion consists of a mixture of sperm and prostate discharge, an increase in volume and darkening may be signs of prostatitis.
Pathological discharge
In men, the causes of discharge from the penis can be sexually transmitted diseases, tumors, nonspecific inflammations of the genitals, various injuries, medical manipulations or surgeries.
Pathological discharge from the urethra differs from normal:
- By volume (very abundant or scanty, perhaps moderate);
- In color and transparency (from white to yellow-green, cloudy);
- From impurities (blood, pus, mucus lumps);
- Consistency (too thin or too thick and sticky);
- From the wind (sour, rotten, fishy);
- By frequency of occurrence (depending on time of day, constant or episodic discharge);
- In connection with urination, sexual arousal, with alcohol intake, spicy and spicy foods.
The nature of the discharge depends on the causative agent of the disease, the state of the immune system, the concomitant diseases, as well as the severity and duration of the inflammation (acute or chronic).
If the amount, density or color of the discharge changes, if an unpleasant odor appears, it is recommended to consult a doctor and do tests. Self-diagnosis is not worth it, it is very difficult to accurately recognize the disease with only one symptom.
Discharge from the penis associated with sexually transmitted diseases
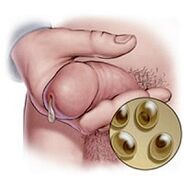
Mucosa: transparent, viscous, small-sized leak found in the chronic form of chlamydia, mycoplasma, or ureaplasmic urethritis. The microscope detects a moderate number of leukocytes in secretions (the rate is up to 4 cells per field of view).
Mucopurulent: white, translucent discharge; observed in the exacerbation phase with chlamydia, ureaplasmosis and mycoplasmosis. In chlamydial infections, they accumulate on the head of the penis, as if "sticking" to the skin.
With the above pathologies, the discharge will come from the urethra itself, as the microorganisms irritate the urethral mucosa and the body tries to "wash it".
It happens that the secret of white color seems to cover the head. This is observed with chlamydia, candidiasis. In the first case, a film is formed, in the second - a loose bloom with cheese.
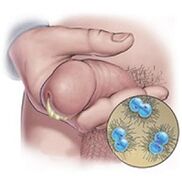
Purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor is characteristic of gonorrhea. They are sticky, thick, yellow or green in color, with a putrid odor. Microscopic examination of the material shows epithelial cells from the urethra, many leukocytes.
Symptoms accompanying gonorrhea urethritis: persistent and profuse discharge; pain, itching and burning are especially severe when urinating.
In sexually transmitted diseases, combined infections are often observed, combining several pathogens at once. Gonorrhea and trichomoniasis are accompanied by chlamydia, mycoplasmosis and ureaplasmosis are commonly found in pairs. The symptomatology of such diseases differs from the classical manifestations; urethral discharge can also take on a completely different character. Therefore, for the final diagnosis, modern analytical techniques with a high degree of reliability are used and not discharge characteristics.
Nonspecific (non-venereal) inflammation.
The cause of nonspecific inflammation is its microflora, which is conditionally pathogenic and is activated only in case of problems with the body's immune defenses. Streptococci and staphylococci, fungi of the genus Candida and E. coli are always present on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes, but they begin to actively multiply and displace beneficial bacteria after hypothermia, prolonged stress, uncontrolled treatment with antibiotics, afterradiation courses. and chemotherapy.
Jogonorreal urethritis (nonspecific). Inflammatory discharges are of small volume, visible in the urine as mucopurulent cords or lumps, appearing at the onset of the disease. Symptoms in the form of burning and itching when urinating are less pronounced than with gonorrhea, but the onset is frequent and brings no relief. With a growing infection, the bladder initially becomes inflamed, followed by the ureters and kidneys; discharge appears with a mixture of red blood.
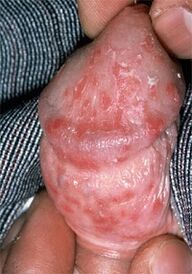
Candidiasis (thrush), a fungal infection of the urethra. It usually develops against the background of suppression of the immune system after a course of antibiotics, chemotherapy or radiotherapy; sexual transmission of candidiasis to men is rare. Thrush is characterized by a sour smell of cottage cheese, which is combined with itching and burning during mixing (urination) and ejaculation (ejaculation), and may be accompanied by dull pain in the groin, above the pubis and in the lower back.
Gardnerelosis of the urethra. The smell of discharge fish is characteristic; they are sparse, white to yellow or green. According to some classifications, gardnerella is referred to as STD, but in men, sexually transmitted infection with gardnerella is more likely a curiosity. In fact, this disease is associated with a violation of the normal microflora, namely dysbiosis. Immunocorrectors and probiotics (lactic acid bacteria) are necessarily used in its treatment.
Balanoposthitis, inflammation of the foreskin. Locally abundant purulent discharge is observed, a mixture of mucus is possible. Always accompanied by edema and hyperemia (redness) of the foreskin leaves, headache of the penis.
With the prostate, a turbid discharge appears at the end of urination, abundant discharge - in the acute period of inflammation; sparse and white - with the passage of the disease into a chronic form. Prostatitis is usually complicated by difficulty urinating and poor erection, in severe cases - up to anuria (complete lack of urine flow) and impotence.
Discharge is not associated with inflammation

Spermatorhea - discharge in the form of passively flowing sperm, occurs outside of sexual intercourse or masturbation, without the sensation of orgasm. The reasons are some diseases of the nervous system, spinal cord injuries, chronic stress and any prolonged inflammation of the genital area. Spermatorhea is accompanied by a violation of innervation and a decrease in the tone of the vas deferens.
Hematorhea, spots. It often appears with urethral canal injuries received during bougiening, after the insertion of a catheter, or when a stain is obtained from the mucosa. In these cases the blood is fresh, without clotting, the amount is small, the bleeding stops quickly. When small stones in the kidneys or sand pass, blood is released during or immediately after urination, hematorrhea is accompanied by very severe pain (renal colic). Discharge of blood in the hematuric form of glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the renal glomeruli) is combined with edema and persistent high blood pressure, the appearance of proteins in the urine.
Brown discharge, with blood clots or mucus, with a mixture of pus appearing in malignant tumors arising from the prostate, urethra, or bladder. Brown mucus may form during wound healing in the mucosa, and is secreted by urethral and / or bladder polyps.
Prostatorrhea is the secretion of the prostate gland derived from the urethra. Occurs in chronic prostatitis, prostate adenoma, impaired innervation (neurogenic bladder).
Examination algorithm in the presence of pathological discharge from the penis
- Examination of the perineum, penis, foreskin and glans. The purpose is to identify the deformities of the genitals, the traces of their damage, the signs of external inflammation, secretions, rashes, etc. Traces of secretions are sometimes observed in freedom.
- Palpation of the inguinal lymph nodes, assessment of their condition: size, they are hotter or colder than the surrounding tissues, painful or not, soft or dense, mobile or attached to the skin, if there are ulcers abovetire.
- Finger examination of the prostate; massaging the prostate through the rectum and taking secretions for microscopic examination. Before the massage, it is advisable to refrain from urinating for 1-2 hours. In the case of prostate adenoma, its lobes grow approximately evenly, dense strands are felt. For a malignant tumor, uneven growths and their consistency are typical; during palpation of the prostate, clotted blood may be released from the urethra.
- Material - stains for microscopy and culture. When examined under a microscope, a stained stain shows blood cells, epithelium, semen, fatty inclusions, some pathogens (Escherichia coli, gonococcus, gardnerella, yeast). An increased number of leukocytes is characteristic of acute urethritis or exacerbation of chronic inflammation, eosinophils - for allergic urethritis. Erythrocytes are found in severe inflammations, tumors, injuries of the genitourinary organs, urolithiasis. A large amount of epithelium is a sign of chronic urethritis, urethral leukoplakia. With spermatorhea, sperm cells are found in a spot, with urethra - mucus, prostatorrhea - lipid grains. For informative content and reliability of results, the stain is taken no earlier than 3 days after topical application of antibiotics, antifungals and disinfectants. If antibiotic treatment was systemic, then at least 3 weeks should pass after the course. Before you get a stain, do not wash, try not to urinate for 2-3 hours.
- General clinical analysis of blood, blood for sugar - in the morning, on an empty stomach. Extended urine analysis (morning part, immediately after sleep).
- Ultrasound of the prostate, bladder and kidneys; CT and urography.
If the manifestations of genital inflammation are strong, then before the test results are obtained, the patient is immediately prescribed antibiotics of a wide spectrum of action. With profuse bleeding, hospitalization and active actions to stop the bleeding are indicated. Confirmation of suspicion of a malignant tumor can only be the result of a biopsy, the final diagnosis is made on the basis of a histological examination.
Important:
- Discharge from the penis is just a symptom that can not be guided when a diagnosis is made.
- Independent naming of the farm is unacceptable. drugs, even if the manifestations seem obvious for a certain disease.